Impact of physical education curriculum on muscular strength of university students
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60081/SSHA.2.2.2024.281-290Keywords:
- Physical Education,
- Hand Grip Strength,
- Public Health,
- Muscular Strength
Abstract
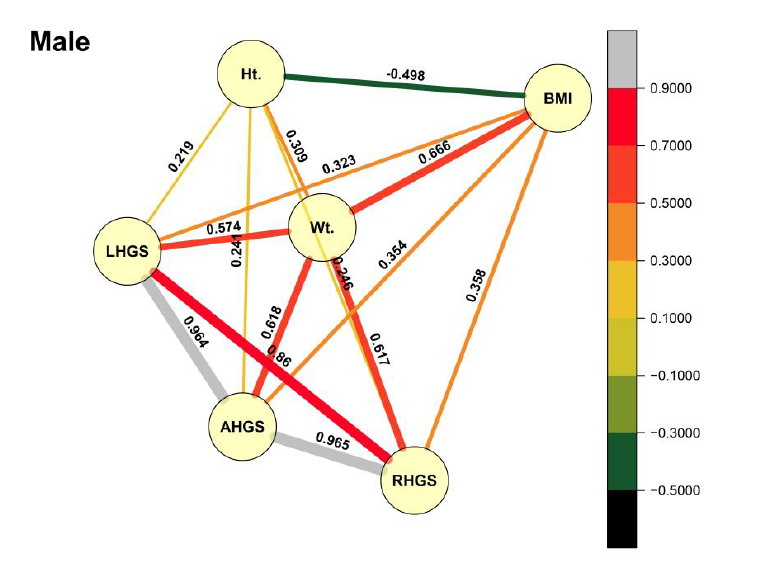
Purpose: Physical education is a subject which improve the overall physical activity and strength of the students in school and college settings. The present study aimed to explore impact of physical education curriculum on the muscular strength in terms of hand grip strength of university students. Methods: A total of 100 university students, both male and female, participated in this study, representing multiple academic departments. Each participant’s physical characteristics, including height, weight, and BMI, were recorded. Hand grip strength was measured using right hand grip strength (RHGS), left hand grip strength (LHGS), and average hand grip strength (AHGS). Statistical analysis was conducted to compare physical parameters across departments and to assess correlations between physical characteristics and grip strength. Additionally, network analysis was used to visualize the interrelationships among variables. Results: The comparison of baseline characteristics between students in Physical Education and other departments showed no significant differences in height, weight, or BMI, indicating that physical characteristics were similar across groups. However, correlation analysis revealed a strong positive association between grip strength and certain physical parameters, particularly weight and height. Network analysis highlighted that, for both male and female participants, weight was significantly correlated with hand grip strength, while height showed moderate associations. These findings suggest that students with higher weight and greater height tend to have stronger hand grip strength. Conclusion: This study demonstrates that physical parameters, especially weight and height, are important determinants of hand grip strength. These factors should be considered when assessing grip strength and designing training programs aimed at its improvement. For practitioners and educators in fields related to physical education and sports science, incorporating weight and height into grip strength evaluation and training can enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of program outcomes. This insight emphasizes the importance of a holistic approach to grip strength development, integrating physical parameters to support optimal strength performance.
Downloads
References
Abe, T., Thiebaud, R. S., Ozaki, H., Yamasaki, S., & Loenneke, J. P. (2022). Children with Low Handgrip Strength: A Narrative Review of Possible Exercise Strategies to Improve Its Development. CHILDREN-BASEL, 9(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/children9111616
Belhaidas, M. B., Dahoune, O., Eather, N., & Oukebdane, M. A. (2023). Objectivity, Reliability, and Validity of the Basketball. Throw Test as a Health-related Measure of Upper-Body Muscular Strength in a Sample of Algerian Primary School Children. MEASUREMENT IN PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND EXERCISE SCIENCE, 27(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/1091367X.2021.2021205
Bellón, D., Rodriguez-Ayllon, M., Solis-Urra, P., Fernandez-Gamez, B., Olvera-Rojas, M., Coca-Pulido, A., Toval, A., Martín-Fuentes, I., Bakker, E. A., Sclafani, A., Fernàndez-Ortega, J., Cabanas-Sánchez, V., Mora-Gonzalez, J., Gómez-Rio, M., Lubans, D. R., Ortega, F. B., & Esteban-Cornejo, I. (2024). Associations between muscular strength and mental health in cognitively normal older adults: a cross-sectional study from the AGUEDA trial. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLINICAL AND HEALTH PSYCHOLOGY, 24(2). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijchp.2024.100450
Busta, J., Coufalová, K., & Cochrane, D. J. (2022). Strength and Strength-Related Anthropometric Parameters of the International Level Canoe Slalom Male Paddlers. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MORPHOLOGY, 40(3), 579–583.
Butovskaya, M. L., Mezentseva, A., Mabulla, A., Shackelford, T. K., Schaefer, K., Fink, B., & Windhager, S. (2022). Facial cues to physical strength increase attractiveness but decrease aggressiveness assessments in male Maasai of Northern Tanzania. EVOLUTION AND HUMAN BEHAVIOR, 43(2), 115–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.evolhumbehav.2021.11.006
Chaput, J. P., Janssen, I., Sampasa-Kanyinga, H., Tomkinson, G. R., & Lang, J. J. (2023). Economic burden of low muscle strength in Canadian adults. APPLIED PHYSIOLOGY NUTRITION AND METABOLISM, 48(8), 634–638. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2022-0371
Confortin, S. C., Barbosa, A. R., de Oliveira, B. R., Magalhaes, E. I. D., Bragança, M., Alves, M., Levy, R. B., Batista, R. F. L., Viola, P., & da Silva, A. A. M. (2022). The consumption of culinary preparations and ultra-processed food is associated with handgrip strength in teenagers. NUTRITION JOURNAL, 21(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12937-022-00818-5
de Souza, M. A., Martinez, E. Z., Lizzi, E. A. D., Cezarani, A., Davoli, G. B. D., Bená, M. I., Sobreira, C. F. D., & Mattiello-Sverzut, A. C. (2022). Alternative instrument for the evaluation of handgrip strength in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. BMC PEDIATRICS, 22(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-022-03388-x
DeHondt, B. G., Madi, S. A., Drignei, D., Buchan, D. S., & Brown, E. C. (2023). Handgrip Strength Cut-Points for Cardiometabolic Risk Identification in U.S. Younger Population. MEASUREMENT IN PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND EXERCISE SCIENCE, 27(3), 224–233. https://doi.org/10.1080/1091367X.2022.2160254
Fenta, B. G., & Mola, D. W. (2023). Effect of eight-week callisthenics exercise on selected physical fitness quality and skill performance in handball. Jurnal SPORTIF: Jurnal Penelitian Pembelajaran, 9(3), 550-566. https://doi.org/10.29407/js_unpgri.v9i3.21335
Garcia, N. F., de Moraes, C., Rebelo, M. A., Peters, S., de Castro, F. M. P., & Puggina, E. F. (2022). Strength training with and without arteriovenous blood flow restriction improves performance, regardless of changes in muscle hypertrophy, in Wistar rats. ANAIS DA ACADEMIA BRASILEIRA DE CIENCIAS, 94. https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765202220201147
Garcia-Hermoso, A., Cofre-Bolados, C., Andrade-Schnettler, R., Ceballos-Ceballos, R., Fernández-Vergara, O., Vegas-Heredia, E. D., Ramírez-Vélez, R., & Izquierdo, M. (2021). Normative reference values for handgrip strength in chilean children at 8-12 years old using the empirical distribution and the lambda, mu, and sigma statistical methods. Journal of strength and conditioning research, 35(1), 260–266. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000002631
Homolak, J., Virag, D., Kodvanj, I., Matak, I., Perhoc, A. B., Knezovic, A., Barilar, J. O., Trkulja, V., & Salkovic-Petrisic, M. (2022). A hacked kitchen scale-based system for quantification of grip strength in rodents. Computers in biology and medicine, 144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105391
Hong, S., Oh, M., Kim, Y., & Jeon, J. Y. (2022). Association of Absolute and Relative Handgrip Strength with Prevalent Metabolic Syndrome in Adults: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2014-2018. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL RESEARCH AND PUBLIC HEALTH, 19(19). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912585
Jeon, Y. J., Lee, S. K., & Shin, C. (2021). Relative Hand Grip and Back Muscle Strength, but Not Mean Muscle Strength, as Risk Factors for Incident Metabolic Syndrome and Its Metabolic Components: 16 Years of Follow-Up in a Population-Based Cohort Study. APPLIED SCIENCES-BASEL, 11(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115198
Kurihara, T., Terada, M., Numasawa, S., Kusagawa, Y., Maeo, S., Kanehisa, H., & Isaka, T. (2021). Effects of age and sex on association between toe muscular strength and vertical jump performance in adolescent populations. PLOS ONE, 16(12). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0262100
Kwon, R. J., Cho, Y. H., Park, E. J., Lee, Y. G., Lee, S. Y., Choi, J. I., Lee, S. R., & Son, S. M. (2024). Relationship between Pulse Pressure and Handgrip Strength in the Korean Population: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study. JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MEDICINE, 13(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051515
Laurson, K. R., Welk, G. J., Saint-Maurice, P. F., & Eisenmann, J. C. (2022). Design and Comparison of Criterion-referenced Standards for Grip Strength in U.S. Children and Adolescents. MEASUREMENT IN PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND EXERCISE SCIENCE, 26(4), 289–296. https://doi.org/10.1080/1091367X.2021.2017292
Lbban, E., Macey, A., Rundle, J., Ashor, A., Idris, I., & Siervo, M. (2024). Effects of dietary nitrate and vitamin C co-ingestion on blood pressure and hand-grip strength in young adults. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR VITAMIN AND NUTRITION RESEARCH, 94(5–6), 342–353. https://doi.org/10.1024/0300-9831/a000799
Lichtenstein, E., Wagner, J., Knaier, R., Infanger, D., Roth, R., Hinrichs, T., Schmidt-Trucksaess, A., & Faude, O. (2023). Norm Values of Muscular Strength Across the Life Span in a Healthy Swiss Population: The Complete Study. SPORTS HEALTH-A MULTIDISCIPLINARY APPROACH, 15(4), 547–557. https://doi.org/10.1177/19417381221116345
Little, B. B., Reyes, M. E. P., & Malina, R. M. (2024). Tracking anthropometric dimensions and grip strength among children, adolescents, and adults in an indigenous community of southern Mexico: 1968-1978-2000. AMERICAN JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL ANTHROPOLOGY, 185(3). https://doi.org/10.1002/ajpa.25017
Lopez-Jaramillo, P., Lopez-Lopez, J. P., Tole, M. C., & Cohen, D. D. (2022). Muscular Strength in Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality: A Narrative Review. ANATOLIAN JOURNAL OF CARDIOLOGY, 26(8), 598–607. https://doi.org/10.5152/AnatolJCardiol.2022.1586
Mausehund, L., Werkhausen, A., Bartsch, J., & Krosshaug, T. (2022). Understanding Bench Press Biomechanics-The Necessity of Measuring Lateral Barbell Forces. JOURNAL OF STRENGTH AND CONDITIONING RESEARCH, 36(10), 2685–2695. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000003948
Meisel, P., Daboul, A., Bnlow, R., Eremenko, M., Völzke, H., Biffar, R., & Kocher, T. (2023). Masticaticatory muscles characteristics in relation to adiposity and general muscular fitness: a population-based study. ODONTOLOGY, 111(3), 742–749. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10266-023-00785-1
Mola, D. W., & Bayeta, G. T. (2020). Effect of circuit training on selected health-related physical fitness components: The case of sport science students. Turkish Journal of Kinesiology, 6(4), 142-148. https://doi.org/10.31459/turkjkin.812512
Mosse, D. (2020). Outside Caste? The Enclosure of Caste and Claims to Castelessness in India and the United Kingdom. COMPARATIVE STUDIES IN SOCIETY AND HISTORY, 62(1), 4–34. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0010417519000392
Nakanishi, S., Shimoda, M., Kimura, T., Katakura, Y., Sanada, J., Fushimi, Y., Iwamoto, Y., Iwamoto, H., Mune, T., Kaku, K., & Kaneto, H. (2024). The impact of grip strength, waist circumference, and body mass index on Hemoglobin A1c value: Cross-sectional study using outpatient clinical data in Japanese elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. GERIATRICS & GERONTOLOGY INTERNATIONAL, 24(4), 410–414. https://doi.org/10.1111/ggi.14864
Noji, Y., Hatanaka, R., Nakaya, N., Kogure, M., Nakaya, K., Chiba, I., Kanno, I., Nakamura, T., Tsuchiya, N., Momma, H., Hamanaka, Y., Orui, M., Kobayashi, T., Uruno, A., Kodama, E. N., Nagatomi, R., Fuse, N., Kuriyama, S., & Hozawa, A. (2024). Association of physiological factors with grip and leg extension strength: tohoku medical megabank community-based cohort study. BMC PUBLIC HEALTH, 24(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18244-z
Ozaki, H., Abe, T., Dankel, S. J., Loenneke, J. P., Natsume, T., Deng, P. Y., & Naito, H. (2021). The Measurement of Strength in Children: Is the Peak Value Truly Maximal? CHILDREN-BASEL, 8(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/children8010009
Rahman, M. H., & Sharma, J. P. (2023). An assessment of maximal isometric hand grip strength and upper body explosive strength and endurance in various ball sports. Physical Education Theory and Methodology, 23(6), 932–939. https://doi.org/10.17309/tmfv.2023.6.16
Ramos, M., Palmeira, L., Oliveira, T., Melo, R., Lopes, C., Carvalho, I., Chagas, D., & Batista, L. A. (2023). Association of handgrip strength with anthropometry of a Brazilian healthy adolescent sample. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND ERGONOMICS, 29(1), 62–69. https://doi.org/10.1080/10803548.2021.2021713
Reza, M. N., Rahman, M. H., Islam, M. S., Mola, D. W., & Andrabi, S. M. H. (2024). Assessment of motor fitness metrics among athletes in different sports: An original research. Physical Education Theory and Methodology, 24(1), 47–55. https://doi.org/10.17309/tmfv.2024.1.06
Seaton, M. P., Nichols, J. F., Rauh, M. J., Kado, D. M., Wetherell, J. L., Lenze, E. J., & Wing, D. (2023). Associations of Lean Mass, Muscular Strength, and Physical Function with Trabecular Bone Score in Older Adults. JOURNAL OF CLINICAL DENSITOMETRY, 26(3). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocd.2023.101370
Siniarska, A., Nieczuja-Dwojacka, J., Grochowska, M., & Koziel, S. (2021). Body structure, muscular strength and living conditions of primary school children in Warsaw. JOURNAL OF BIOSOCIAL SCIENCE, 53(1), 98–107. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021932020000061
Smith, L., Sánchez, G. F. L., Soysal, P., Veronese, N., Gibson, P., Pizzol, D., Jacob, L., Butler, L., Barnett, Y., Oh, H., Shin, J. I., & Koyanagi, A. (2024). Association of handgrip strength with suicidal ideation among adults aged ≥50 years from low- and middle-income countries. SUICIDE AND LIFE-THREATENING BEHAVIOR, 54(3), 606–614. https://doi.org/10.1111/sltb.13071
Takahashi, R., Nojiri, H., Ohara, Y., Fujiwara, T., & Ishijima, M. (2024). Decreased grip strength is associated with paraspinal muscular oxidative stress in female lumbar degenerative disease patients. JOURNAL OF ORTHOPAEDIC RESEARCH, 42(10), 2287–2295. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.25863
Triana-Reina, H. R., Ortiz-Pacheco, L. E., & Ramírez-Vélez, R. (2022). Lower grip strength values are associated with increased levels of adiposity and excess weight: a cross-sectional study. NUTRICION HOSPITALARIA, 39(4), 752–759. https://doi.org/10.20960/nh.04004
Tsuburai, T., Komase, Y., Tsuruoka, H., Oyama, B., Muraoka, H., Hida, N., Kobayashi, T., & Matsushima, S. (2022). The relationship between peak inspiratory flow and hand grip strength measurement in men with mild chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. BMC PULMONARY MEDICINE, 22(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-022-01858-7
Wu, M. Y., Shu, Y. L., & Wang, Y. J. (2022). Exposure to mixture of heavy metals and muscle strength in children and adolescents: a population-based study. ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE AND POLLUTION RESEARCH, 29(40), 60269–60277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19916-2
Xu, T. J., Li, X., Wang, D. F., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Q. H., Yan, J. Y., Jiang, J. H., Liu, W. B., & Chen, J. (2023). Hand grip strength should be normalized by weight not height for eliminating the influence of individual differences: Findings from a cross-sectional study of 1,511 healthy undergraduates. FRONTIERS IN NUTRITION, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.1063939
Yuan, S. Y., Chen, X. X., Lin, H. J., Shi, R. Z., Li, J., Xu, L. L., Qiao, S. J., Ding, Y. Y., & He, N. (2022). Interaction of declined handgrip strength and HIV infection on neurocognitive impairment. JOURNAL OF NEUROVIROLOGY, 28(2), 217–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-021-01036-1
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Habtamu Feyisa Degefa, Deepak kumar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




